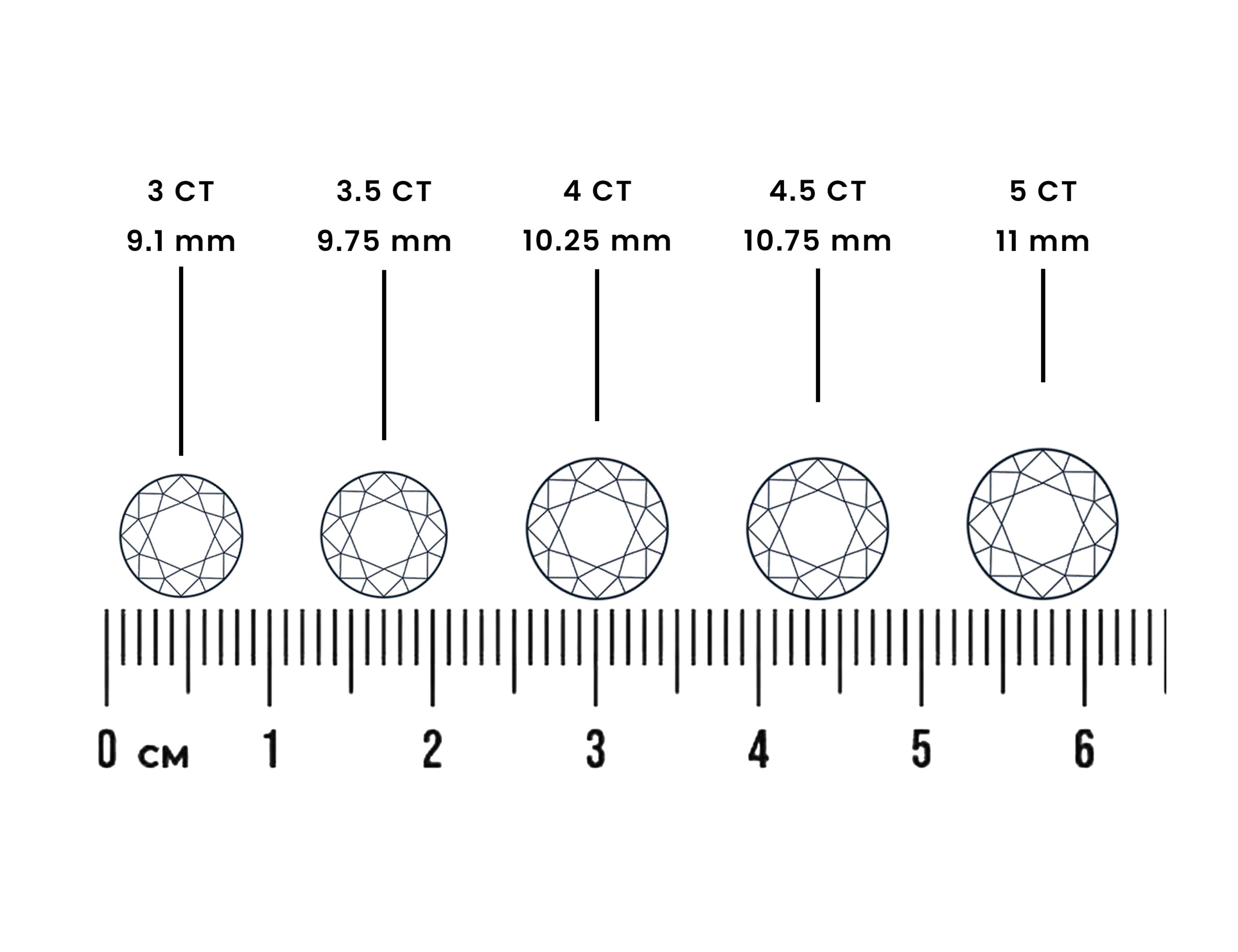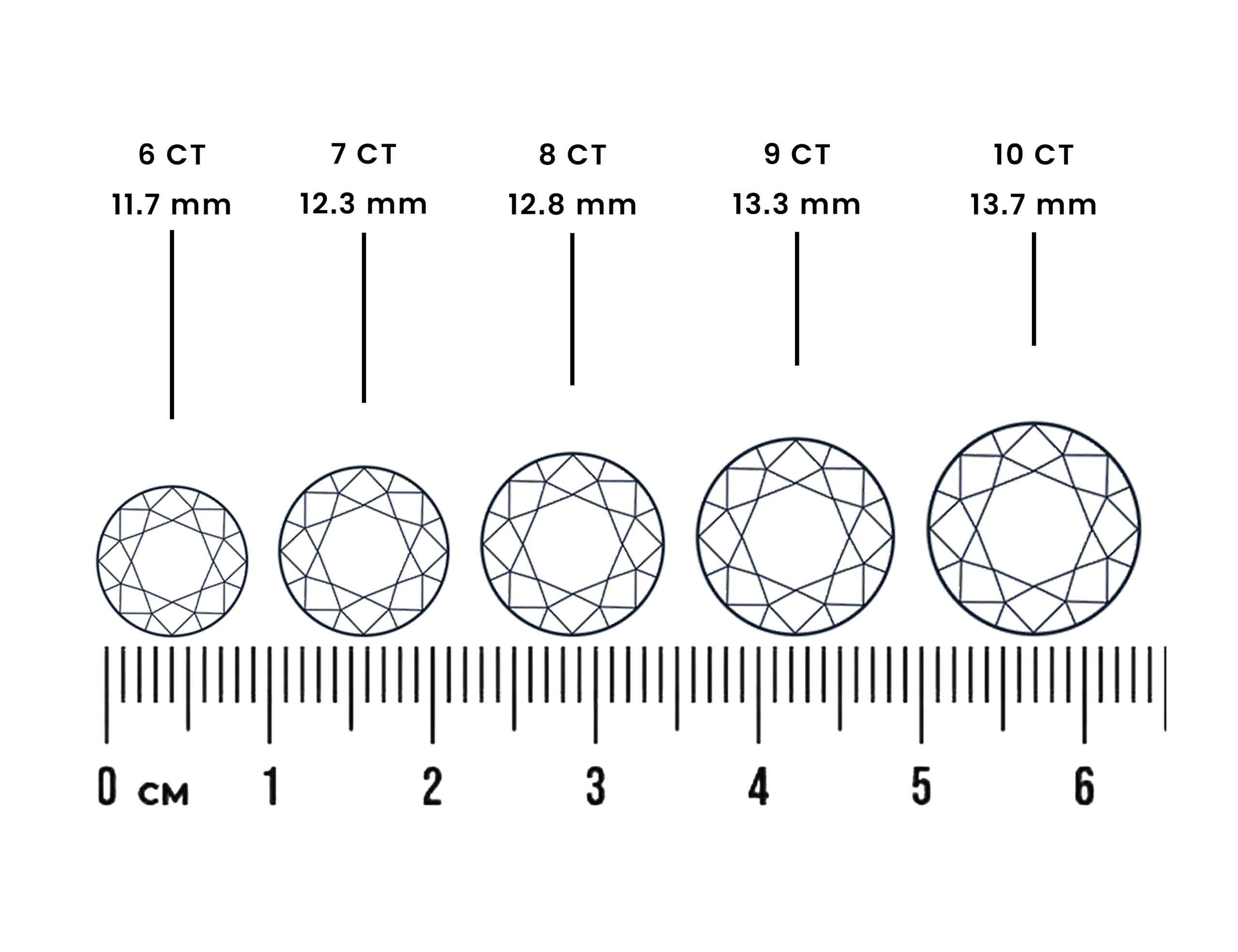
Diamond Color


These diamonds are nearly colorless. Any tint they have is hard to see. Best value for money; large stones available at low prices.

These slightly tinted diamonds are nearly colorless, especially when set in rose and yellow gold.
Diamond Color
Diamond color is graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown).
-
Colorless diamonds (D-F) are the most valuable and rare.
-
Near-colorless (G-J) diamonds offer great value with minimal visible color.
-
Faint to Light Color (K-Z) diamonds have a noticeable yellow or brown tint.
For lab-grown diamonds, color consistency is better controlled compared to natural diamonds. However, it’s still crucial to check the grading to ensure the diamond has the desired level of whiteness.